FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
all information concerns Poland
1. Is obtaining a building permit required for the installation of electric vehicle charging stations?
-Obtaining a building permit is not necessary, however, the installation of charging stations must be reported to the relevant administrative and building authorities.
2. Which chargers are subject to testing conducted by the Technical Inspection Authority (UDT)?
-According to UDT regulations, charging stations and points that are part of public charging infrastructure undergo technical safety and operation tests conducted by the Technical Inspection Authority.
21. How to verify your electrical installation before placing an order?
-To determine the power connection of a building, it is advisable to check the contract with the supplier or directly contact the energy provider, providing your customer number. Contracted power may also be found on electricity bills.
3.How long does the UDT inspection take?
-The Technical Inspection Authority has 30 days to process the application after it has been submitted.
4. I live in a multi-family building - what should I do in such a situation?
-You need to obtain permission from the homeowners' association or cooperative.
Account set up and management
1. Do I need to create an account in the store to place an order
-Yes, by registering, you gain the ability to view your order history.
2. How to create an account in the store?
-You can create an account in the store through the subpage. SIGN UP
3. Can I place an order over the phone or via email?
-Of course, there's no problem at all. Please contact us via phone: +48 510 122 381 or email: sprzedaz@edfplugin.eu
4. How to check the status of my order?
-You can check the status of your order by logging into your user account. If you have any doubts, feel free to contact us via the contact form or email: sprzedaz@edfplugin.eu.
5. Where to check the order history?
-You can check the order history by logging into your user account under the Orders tab.
1. What are the differences between AC and DC charging stations?
- The significant difference lies in the power and charging speed of the vehicle. When using an alternating current (AC) charger, the vehicle charging process will take more time compared to a direct current (DC) charger..
2. Which charger would be suitable for home use?
- In home settings, small AC charging stations, such as wallbox chargers, are particularly effective.
3. Is every charging station compatible with any electric vehicle?
- No, before choosing a charging station, it's important to check if it is equipped with the appropriate connectors for the sockets in your vehicle. If you have any doubts, feel free to reach out to us!
4. Am I able to install a charging station at home or at my company by myself?
-Yes, of course, it's possible to install a small electric vehicle charging station by yourself. However, we recommend that such work be carried out following building codes and manufacturer recommendations. Feel free to reach out to us if you have any doubts!
5. What are the differences between charging a car using an extension cord plugged into a standard socket and charging with a charging station?
-Charging an electric car from a standard socket takes significantly more time compared to using a charging station. It may take several hours to fully charge the car, which is often impractical considering limited available time.
6. How much does it cost to fully charge an electric car at home?
-The cost of charging an electric car at home depends on the rate we pay to the electricity provider for each kilowatt-hour (kWh). Roughly, assuming a cost of 0.5 groszy per kWh, fully charging a 50 kWh battery would only amount to 25 złotys.
7. What factors affect energy consumption in an electric car?
-The topography of the route (uphills increase energy consumption, while descents and regenerative braking can partially recover energy),
-The external temperature (in cold weather and continuous use of heating, the car's range can significantly decrease),
-Factors such as the driver's driving style (greater driving dynamics, higher speeds = increased energy consumption) also influence this,
8. How far can an electric car go on a single charge?
-The maximum range of an electric vehicle depends on the specific model and battery capacity. Smaller models currently cover about 130 km, while the average range of a larger electric vehicle falls between 200 to 400 km. However, it's always important to consider the manufacturer's declared range, taking into account various factors that may affect range limitation, such as driving style, temperature, and terrain.
9. How often should charging station servicing be carried out?
-To maintain the charging station in good condition and ensure safe operation, it is recommended to service it once a year.
10. Can you use a charger with higher power than recommended by the car manufacturer, and is there a risk of damage?
-You can adapt a larger charging station; however, it's important to remember that the car will still be charged according to the power of its built-in charger, which prevents potential battery damage.
11. Is overnight charging cheaper?
-It depends on the energy tariff being used. When using a night tariff, electricity costs will be lower, of course
12. What will happen if I drive while the charger is still plugged in?
In most vehicles, if the charging cable is connected, for safety reasons, it's not possible to drive the car.
13. Tak, można odłączyć wtyczkę ładowania, gdy samochód jest zamknięty.
-Removing the plug is impossible because there is a lock in the vehicle preventing the plug from being disconnected when the car is locked.
14. Can using a charger purchased outside the dealership, without the car manufacturer's logo, harm the vehicle's battery?
-No, nothing will happen as long as we use another charging station with appropriate parameters. Independent manufacturers offer chargers with higher power and additional features, such as Wi-Fi control, etc.
15. Will my charging station be compatible with a different vehicle model when changing cars?
-Yes, because we connect the car to the charging station using a cable. Most charging stations and European electric cars are equipped with Type 2 connector plugs. We also offer adapters from Type 2 to Type 1 if needed.
22. What to do if I accidentally purchase the wrong charger?
-Charging stations with a Type 2 connector are universal and compatible with most electric vehicles. However, if such a situation arises, please contact us before proceeding with the installation of the charger.
23. Can I charge my EV at home if I don't have a charging station?
-Yes, you can charge from a standard Schuko or CEE socket using a charging cable with a control box
25. I will buy the station, and then what?
-For our customers, we offer full support throughout the entire implementation process, from assistance in selecting the device, through concept development, to installation and after-sales service support, including post-warranty assistance.
KNOWLEDGE BASE
TYPE 1 AND TYPE 2
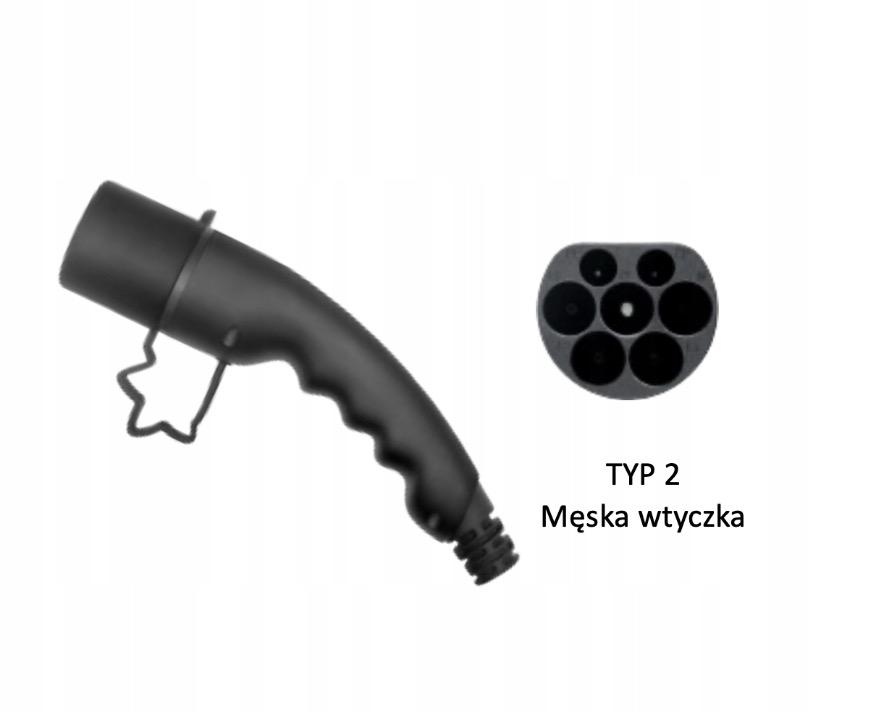
There are two main types of plugs available for charging electric vehicles on the market – Type 1 and Type 2. Distinguishing between them is relatively straightforward, as all newer models of European cars manufactured after 2019 utilize the Type 2 plug standard. This is the most widespread standard for charging electric vehicles in Europe, defined by the IEC 62196-2 norm. Type 2 has the advantage of being available in both single- and three-phase versions, enabling the delivery of a maximum power of up to 22 kW (compared to Type 1, which offers 7.4 kW). Another strength is its full compatibility. Type 2 complies with the Combined Charging System (CSS) standard, commonly known as 'Combo 2.' This allows for the connection of both alternating current (AC) chargers and high-performance direct current (DC) chargers to the same connector, providing additional convenience and flexibility. Type 2 supports charging with alternating current up to 32 A and voltage up to 250V (single-phase) or up to 480V (three-phase). Type 1 is a type of electric vehicle charging socket originating from the North American market, and is used in vehicles offered there. It is also present in selected Asian and even European models. It allows for charging exclusively with alternating current (AC), single-phase, not exceeding 32 A, and voltage up to 250V.
Typ 1 to rodzaj gniazda ładowania pojazdów elektrycznych pochodzący z rynku północnoamerykańskiego i stosowany w oferowanych tam pojazdach. Jest także obecny w wybranych modelach azjatyckich, a nawet europejskich. Pozwala na ładowanie wyłącznie prądem zmiennym (AC), jednofazowym, nie przekraczającym 32 A i napięciem do 250V.
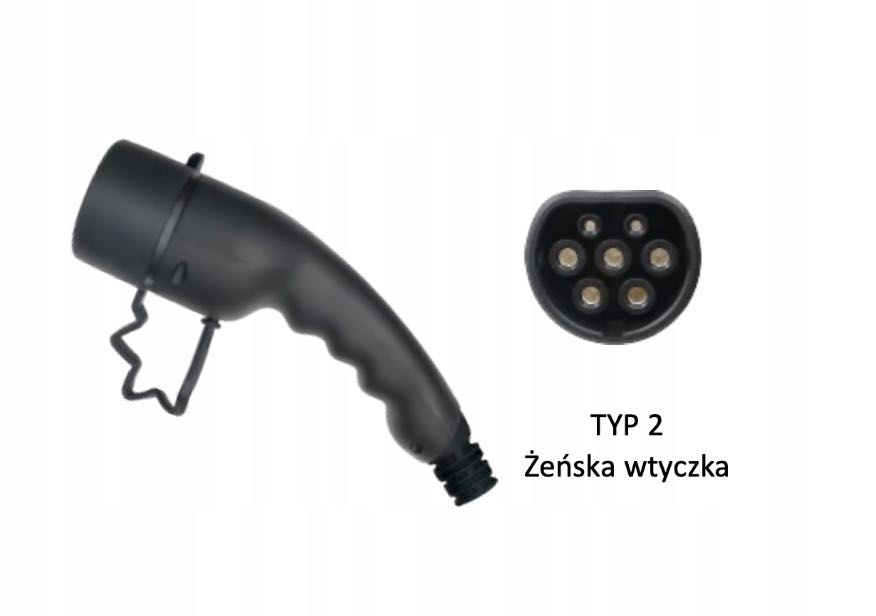

How fast does a 22 kW AC charging station charge?
A 22 kW AC charging station can fully charge a vehicle in a short amount of time, especially when it's equipped with the appropriate socket. For instance, an electric vehicle with a 40 kWh battery can be fully charged in about two hours. However, charging time depends on various factors, such as the state of the battery charge. Regularly plugging in can reduce charging time.
How long does charging take with a 30 kW DC charger?
Using a 30 kW DC charger, a vehicle with a 60 kWh battery can be charged in about two hours. This is possible due to the direct transmission of direct current (DC) to the battery, which speeds up the charging process. 30 kW DC charging stations are particularly useful in locations where drivers need fast charging, such as at fuel stations or parking lots near shopping centers.
How does charging work with a 120 kW DC station?
Charging stations with a power of 120 kW DC are among the most powerful ones currently available. They can charge most electric vehicles from 0 to 80% in about 30 minutes, which is an impressive result. Such stations are particularly useful on highways and at fast charging points, allowing drivers to quickly get back on the road.
Charging time from an outlet
Using an outlet for charging electric vehicles is the slowest but most economical solution. Mobile chargers with a power of 2-3 kW can charge a 60 kWh battery in 20-30 hours. Although the charging speed is low, it is an available and economical option without the need for additional infrastructure installation.
In summary, more powerful chargers shorten charging times, and DC chargers offer the highest speed. Each option has its advantages, and the choice depends on the needs and availability of charging infrastructure.
On the market, there are numerous electric vehicle charging stations available, differing in the type of current (AC, DC) and form (compact, free-standing). When choosing, it's worth paying attention to the size of the station to ensure it doesn't take up too much space in the garage.
It's also worth considering how often and in what way we will use the charger. Different models use different currents, which affects charging time. Therefore, it's important to tailor the device to your own preferences and driving style.
For private use, a good choice might be a compact Wallbox station, easy to mount on the wall, space-saving, and allowing continuous vehicle charging. An alternative could be a compact AC charger, ideal for overnight charging.
The installation of a charging station requires professional assistance, especially due to the high voltage involved. It is advisable to consult with the manufacturer or a specialist with SEP qualifications. Self-installation is only possible for individuals with the appropriate knowledge and qualifications.
In summary, the selection and installation of electric vehicle charging stations should be carefully considered, taking into account individual needs and the safety of the installation.
Modern charging cables for electric vehicles are a crucial component for such vehicles. Below, we will discuss basic information about EV cables, their functions, and the various types available.
The charging cable for an electric vehicle is a specialized wire that connects the car to the charger. Its main task is to transmit electrical energy from the charger to the vehicle's battery. Depending on the type of charger, the cable may be built into the device (e.g., in a wallbox) or be a separate element that needs to be connected to both devices.
During the charging process, the cable transmits electrical current from the charger to the vehicle's battery, ensuring a controlled and safe process. There are various types of cables available on the market, each with different parameters such as plug type, charging power, cable length, and cable type.
Important criteria for choosing a cable include the plug type (e.g., Type 1, Type 2, CCS, CHAdeMO) and charging power (e.g., 7.4 kW, 11 kW, 22 kW). Also, remember to consider the cable length to adapt it to the location where the vehicle is most frequently charged. Additionally, by checking the IP (Ingress Protection) rating, we ensure that the cable is resistant to weather conditions. It's also important to provide adequate protection against overheating and surges.
When making a purchase, it's important to pay attention to the manufacturer's warranty and pre- and post-purchase support to ensure the quality and durability of the product. Choosing the right cable for charging an electric vehicle is crucial for a safe charging process, and customizing it to your own needs ensures efficient use.
You did not find an answer? Write to us!
If you did not find the answer you were looking for in the provided questions and answers, please reach out to us, and we'll respond to all your inquiries.